Extended ER Features
Read This on Github
⭐ Extended ER Features ?
Extended ER Features
In Entity-Relationship (ER) modeling, extended ER features such as specialization and generalization allow modeling of more complex relationships between entities.
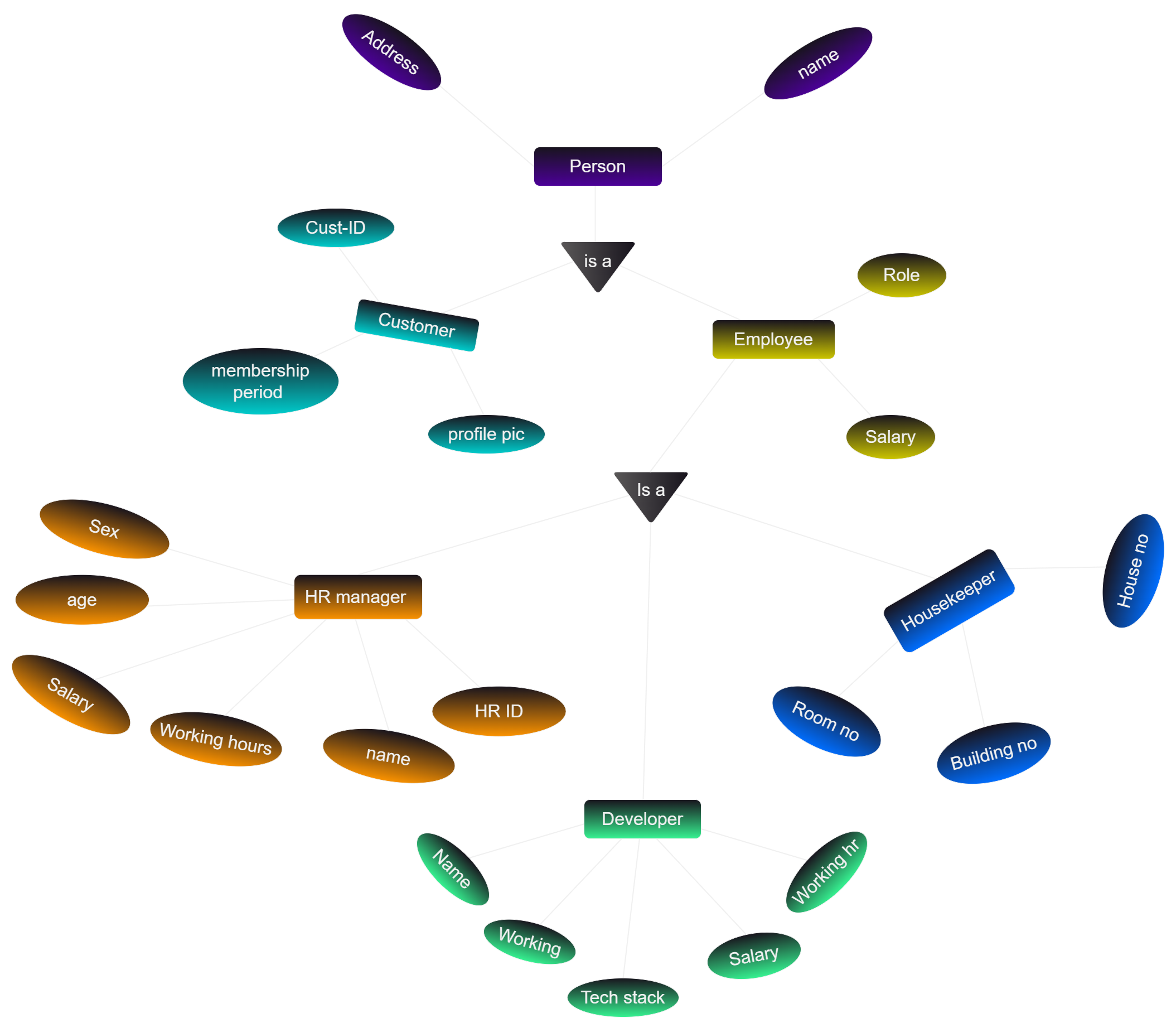
Specialization represents a subtype-supertype relationship where a subtype is a specialized form of a supertype. For example, consider a company that has both permanent and contract employees. Here, the supertype "Employee" can be specialized into "Permanent Employee" and "Contract Employee."
Generalization, on the other hand, represents a supertype-subtype relationship where a supertype is a generalized form of one or more subtypes. For example, consider a company that has both employees and customers. Here, the subtypes "Employee" and "Customer" can be generalized into the supertype "Person."
By using these extended ER features, it is possible to capture the complex relationships between entities, leading to a more accurate and detailed representation of the data. This can lead to better decision making and increased efficiency in processing and retrieving data.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
⭐ Specialisation
Specialisation with Example
Just think about it if you create a person entity and use multiple attributes like "Salary" , " Profile Pic" , " Name" , "Contact" , "Address" , "Contact ID" the complexity of the entity will increase and it will be difficult to manage the data. So, we can create a new entity called "Employee" and use the attributes of the "Person" entity in the "Employee" entity. This is called Specialisation. So It is better to use some extended ER features to model the DB Schema.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
It is a Top-Down approach because you can see that the "Employee" entity is a part of the "Person" entity. So, the "Employee" entity is a subtype of the "Person" entity. So Person is superclass and other specialised entity sets are subclasses.
Specialisation is splitting up the entity set into further sub entity sets on the basis of their functionalities, specialities and features.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
- We have “is-a” relationship between superclass and subclass.
- Depicted by triangle component.
- Higher-level entities and lower-level entities can be linked.
Why we use Specialisation ?
-
Certain attributes are common to all the subclasses so may only be applicable to a few entities of the parent entity set.
-
DB designer can show the distinctive features of the sub entities.
-
To group such entities we apply Specialisation, to overall refine teh DB blueprint.
✅ Specialisation Breakdown
1. Entities Before Specialization
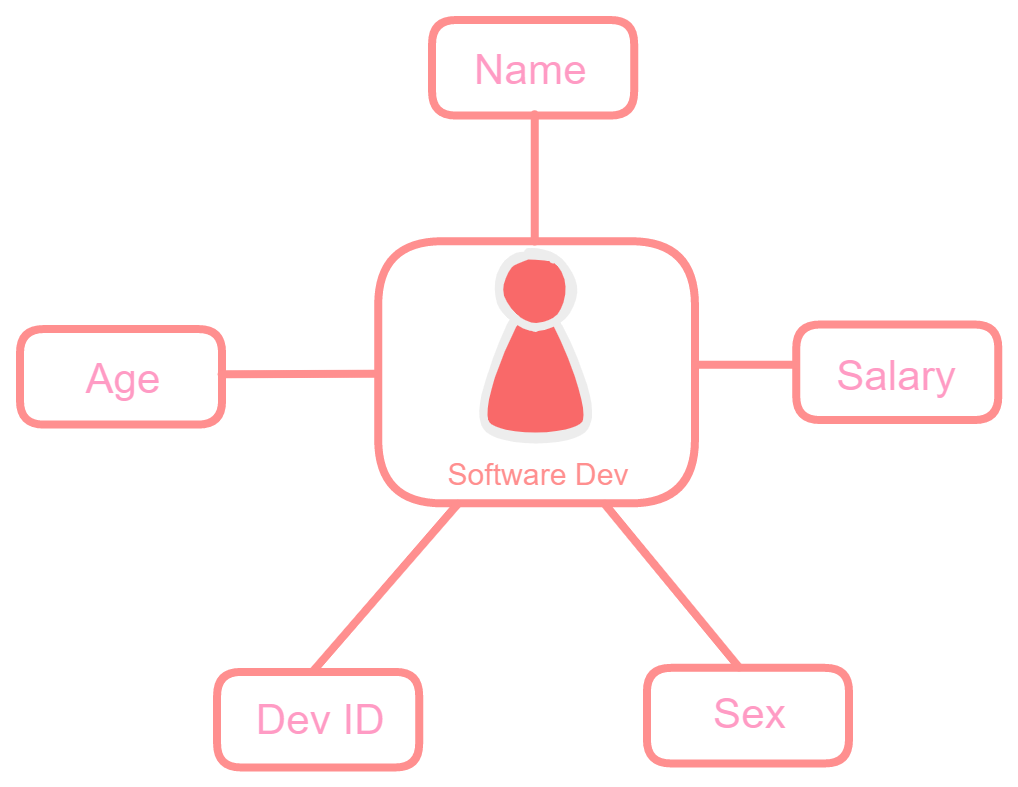
Developer: Software developers can have attributes like name, age, salary, etc. We will apply specialization to this entity and will divide it into entities.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
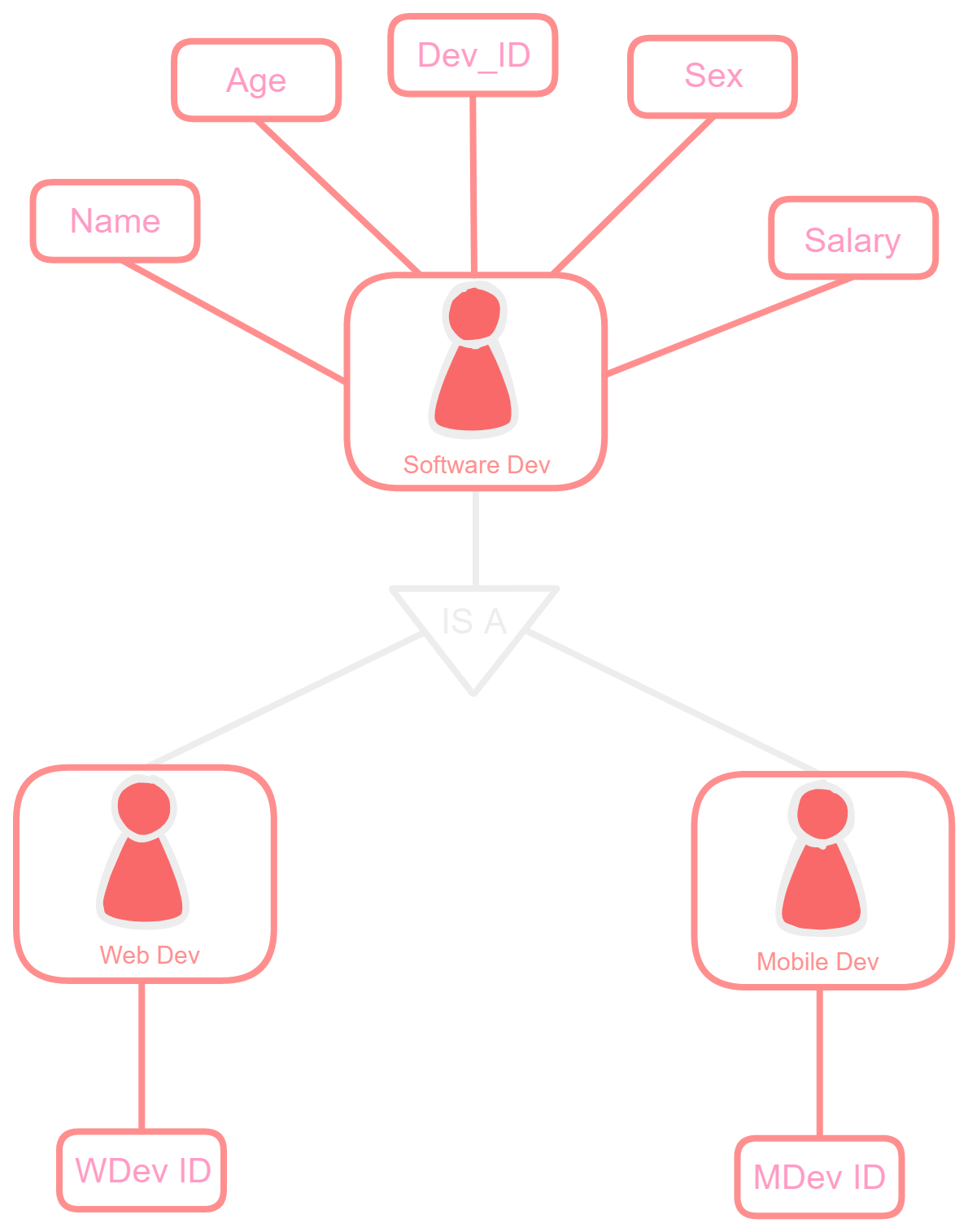
2. ER Diagram after Generalization
We can specialize the software developer entity into mobile developer entity and web developer entity.
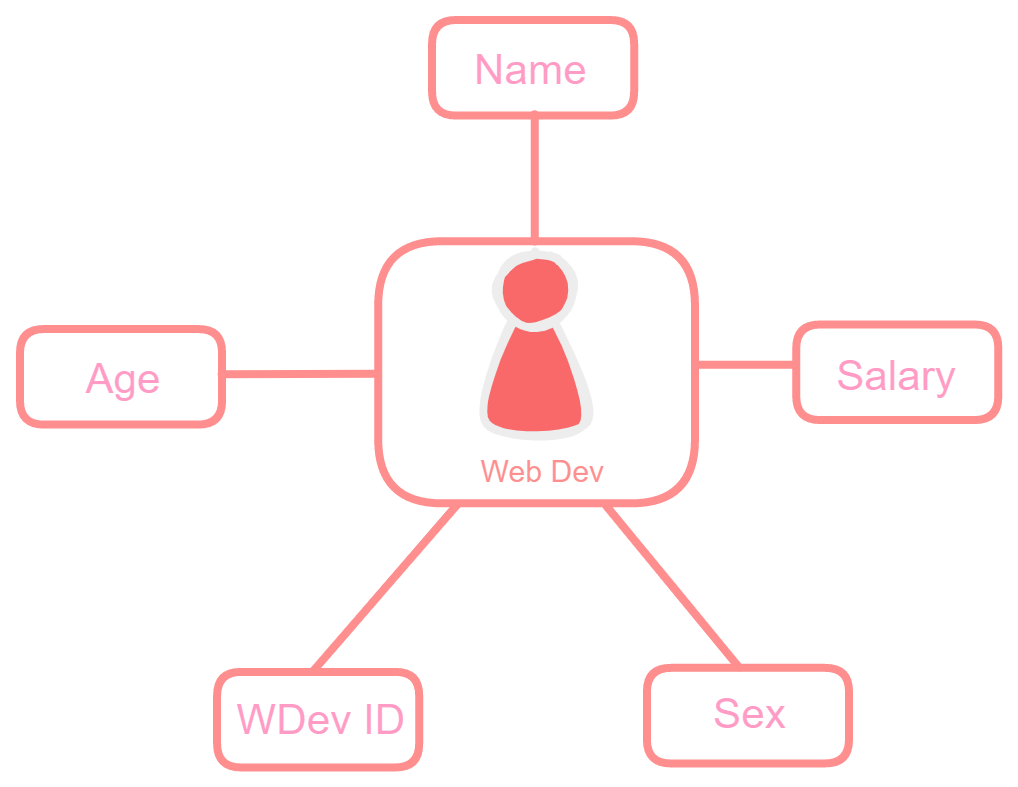
Web Developer Entity: A web Developer entity can have attributes like name, age, salary, and sex and is obtained after applying specialization in a software developer entity.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
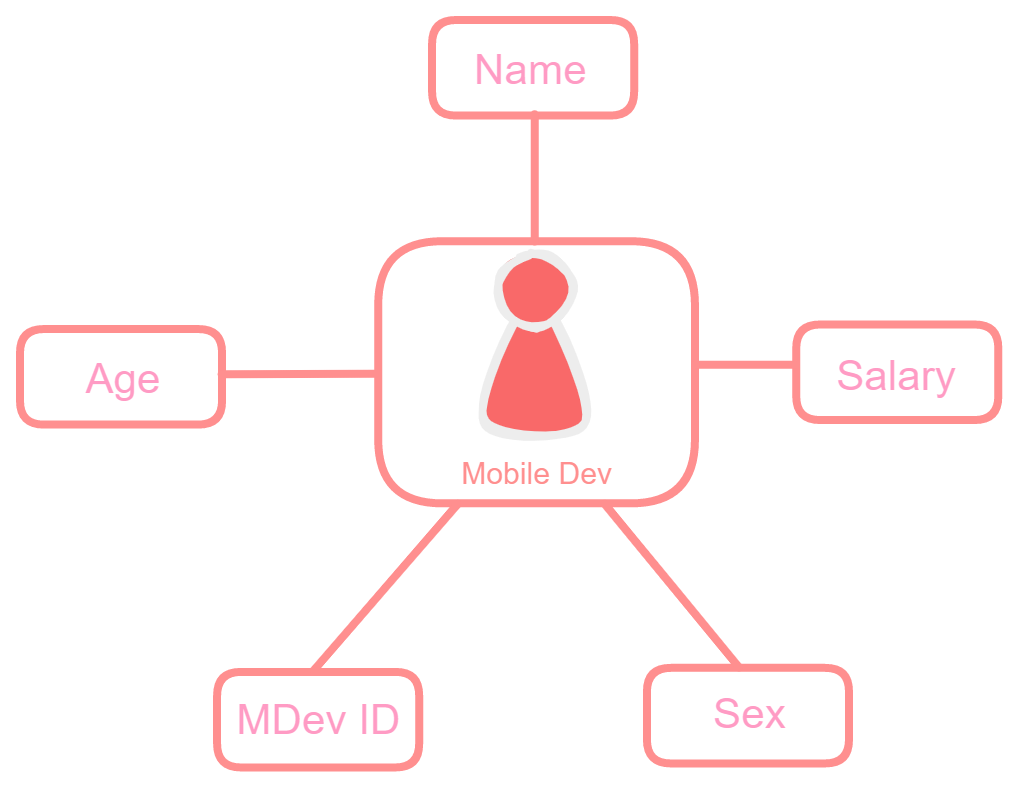
Mobile Developer Entity: Mobile Developer entity can have attributes like name, age, salary, and sex and is obtained after applying specialization in software developer entity.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
3. The ER diagram
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
⭐ Generalization
Generalization
Generalization is a bottom-up approach in which multiple lower-level entities are combined to form a single higher-level entity. Generalization is usually used to find common attributes among entities to form a generalized entity. It can also be thought of as the opposite of specialization.
- It is just a reverse of Specialisation.
- It is a bottom-up approach.
- DB Designer, may encounter certain properties of two entities are overlapping. Designer may consider to make a new generalised entity set. That generalised entity set will be a super class.
- "is-a" relationship is present between subclass and super class.
- e.g., Car, Jeep and Bus all have some common attributes, to avoid data repetition for the common attributes. DB designer may consider to Generalise to a new entity set "Vehicle".
Why we use Generalisation ?
-
Makes DB more refined and simpler.
-
Common attributes are not repeated.
✅ Generalization Breakdown
1. Entities before Generalization
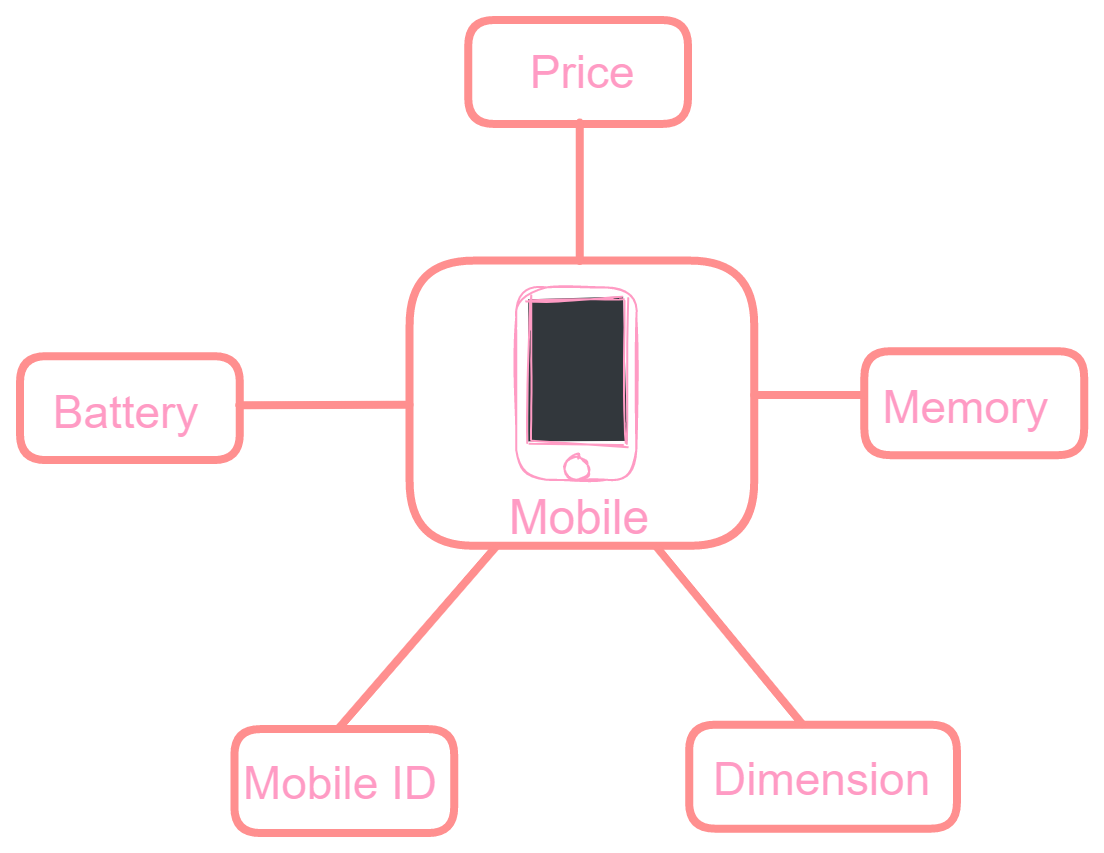
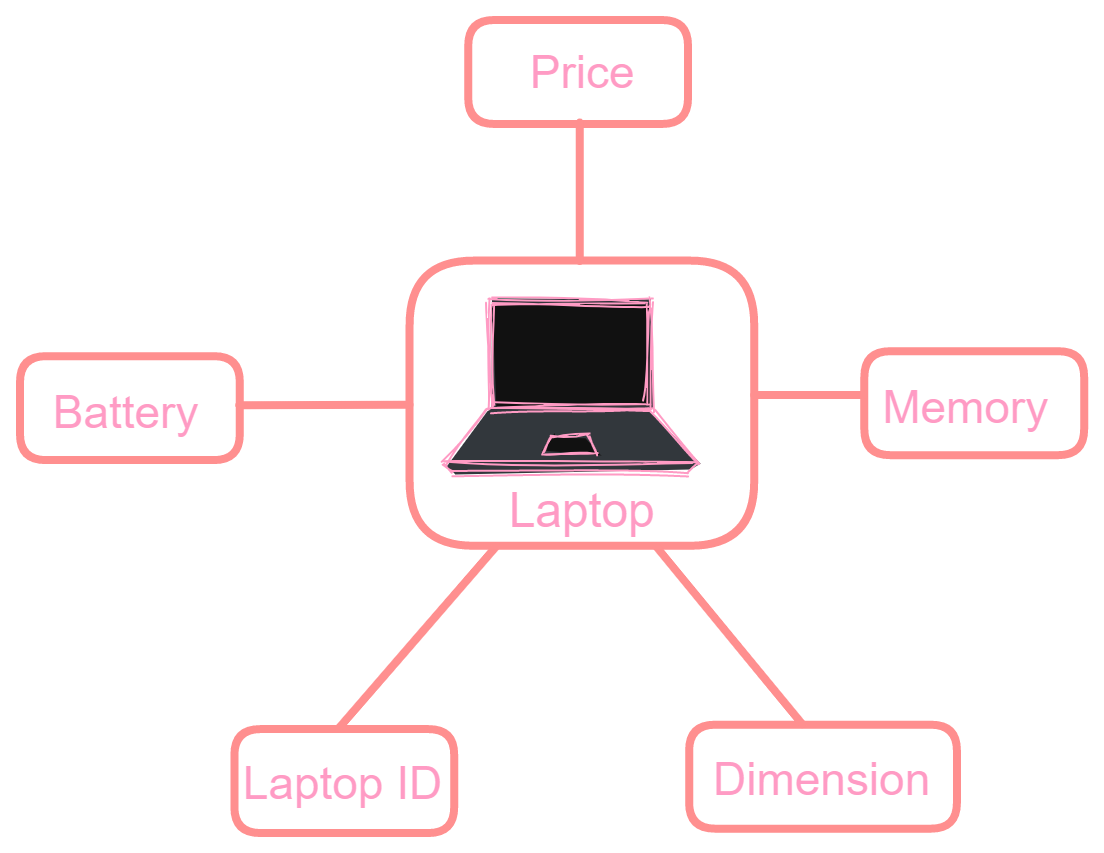
Mobile Entity: Mobile entity can have attributes like mobile_ID, price, memory, battery, and dimension to which we can apply the generalization procedure.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
Laptop Entity: Laptop entity can have attributes like laptop_ID, price, memory, battery, and dimension to which we can apply the generalization procedure.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
2. ER Diagram after Generalization
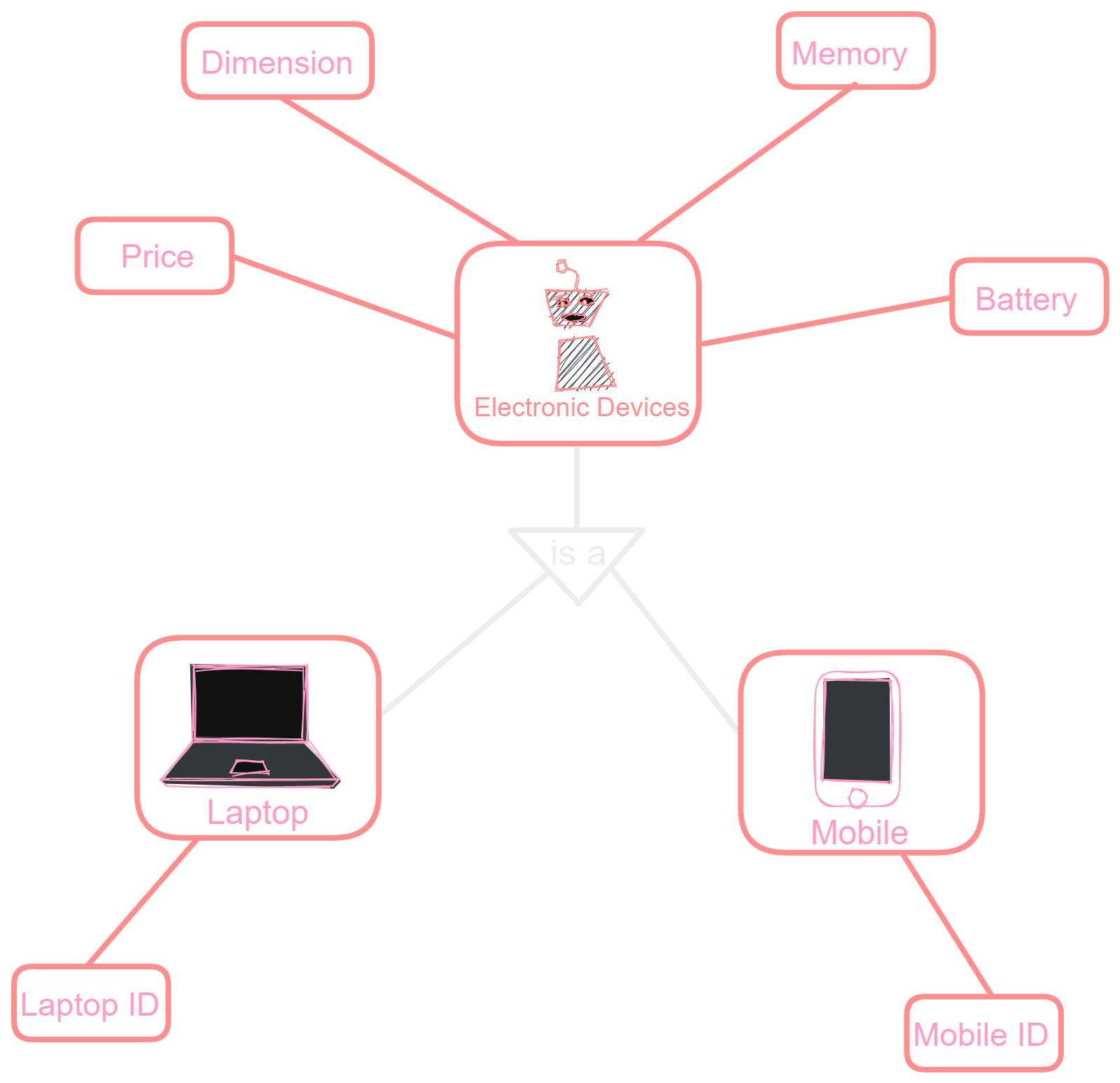
We can see that for laptops and mobiles some attributes like price, memory, battery, and dimension are the same so we can apply generalization and can group them into an entity called Electronic Devices.
The *Electronic Devices entity will be having these common attributes and the laptop and mobile entity will be related to them using "Is A" relationship table, so using generalization we can represent ER diagram by:
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
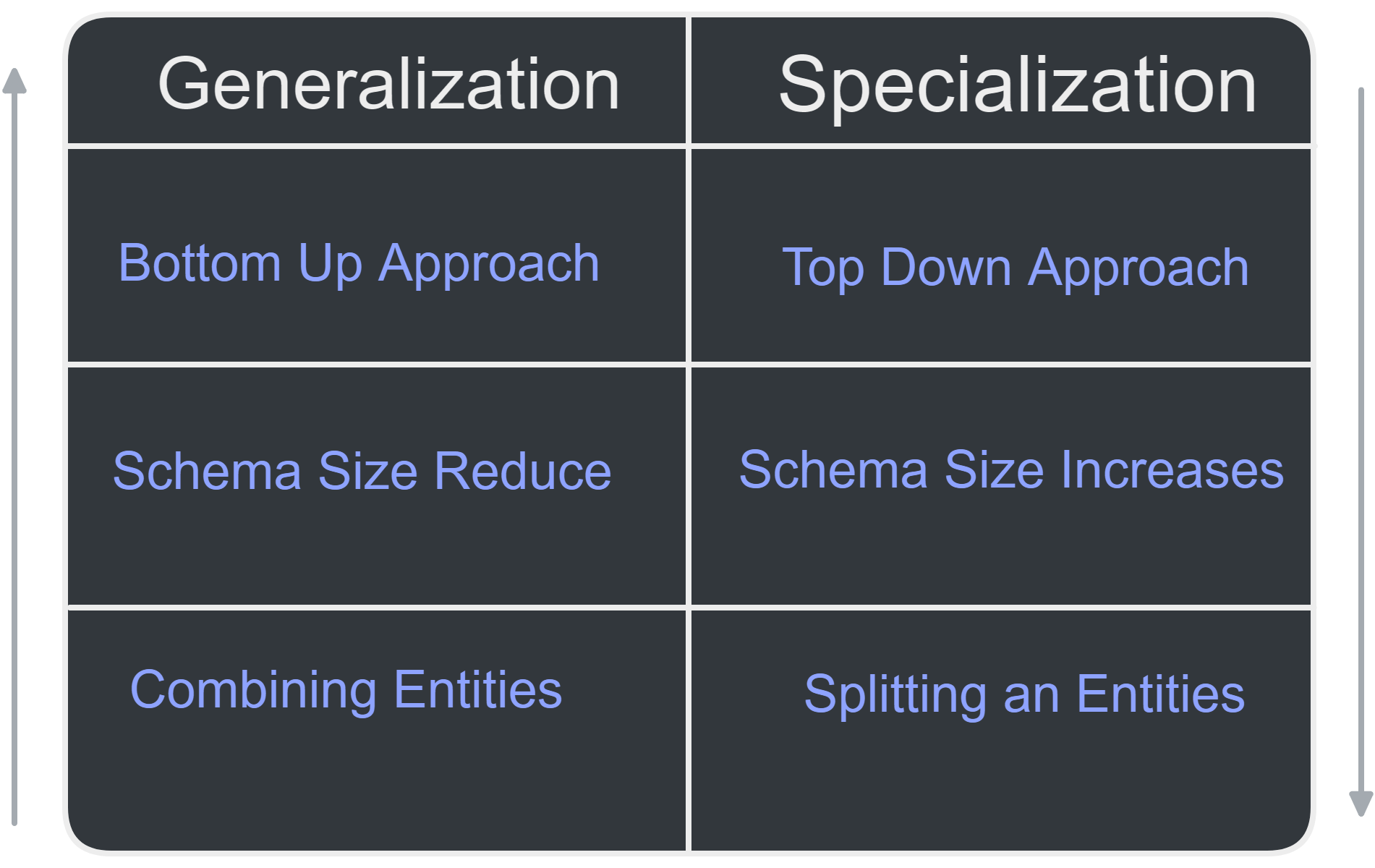
⭐ Generalization vs Specialization vs Aggregation
Generalization vs Specialization vs Aggregation
Generalization vs Specialization vs Aggregation in DBMS
| Concept | Generalization | Specialization | Aggregation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Bottom-up | Top-down | N/A |
| Process | Combining multiple entities into one | Dividing an entity into multiple entities | Grouping multiple entities together to form a single entity |
| Relationship | Higher level entity must have lower level entities | Higher level entity may not have lower level entities | N/A |
| Schema Size | Reduced | Increased | Increased |
| Target | Group of entities | Single entity | Multiple entities |
| Result | Single entity from multiple entities | Multiple entities from a single entity | Single entity from multiple entities |
| Inheritance | Not used | Can be used | Not used |
| Purpose | Visualizing bigger picture patterns | Narrowing search | Grouping entities for simplicity or performance optimization |
⭐ Attribute Inheritance
Attribute Inheritance
If an entity set has a parent entity set then the attributes of the parent entity set are inherited by the child entity set.
- Both Specialisation and Generalisation, has attribute inheritance.
- The attributes of higher level entity sets are inherited by lower level entity sets.
- E.g., Customer & Employee inherit the attributes of Person.
⭐ Participation Inheritance
Participation Inheritance
For example, if person has vehicle then it inherits by customer and employee.
- If a parent entity set participates in a relationship then its child entity sets will also participate in that relationship.
⭐ Aggregation
Aggregation
Aggregation in DBMS(Database Management System) is a process of combining two or more entities that cannot be used alone, to form a more meaningful entity. When a single entity alone doesn't make sense on its own in a relationship then the aggregation process is done and the relationship of two entities acts as one entity after the aggregation has been done. Let's consider a classic example to understand the aggregation in DBMS.
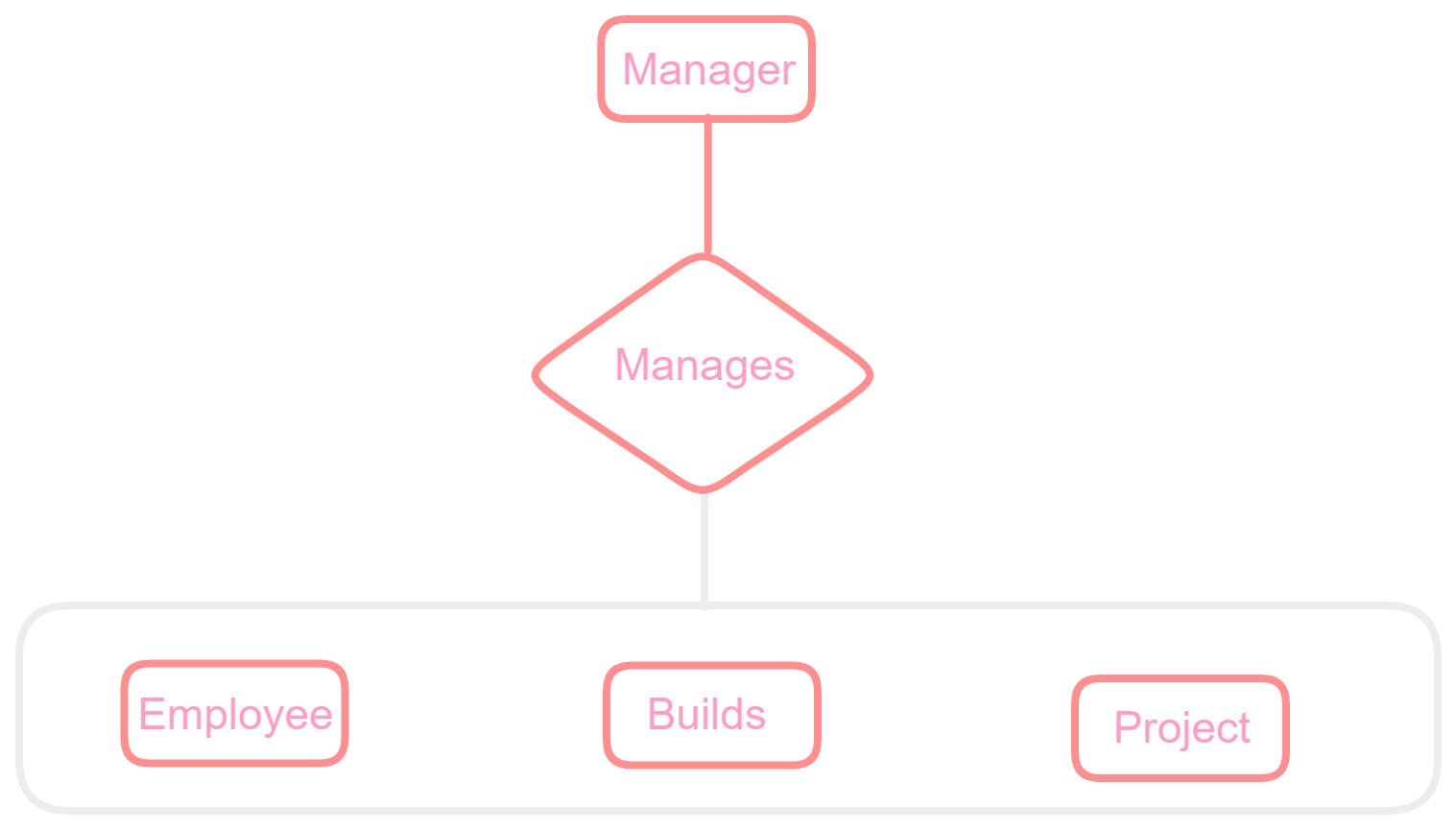
Example: Consider the above structure and let's take an example of an employee and his manager, and the employee working on a project which is also managed by his manager. In a real scenario, you know that a manager not only manages the employee under them but he has to manage the work undertaken by the employee and the project as well. As discussed in the above example, if the "Manager" makes a relationship - "manages" with either "Employee" or "Project" entity alone then it will not make any sense because a manager has to manage both the employee as well as the project, similarly, it can be said that if a single entity cannot derive results alone then it can be aggregated with another entity to form a meaningful relationship. So in this case, a new relationship is formed between the two entities, "Employee" and "Project", the relationship between the two entities acts as one entity. In the given example the relationship "Builds" between the two entities - "Employee" and "Project" acts as one entity that has the relationship "Manages" with the manager.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
Change the image size by using the click-and-scroll function.
Why Use Aggregation in DBMS ?
- At times, the database might contain some entities which are less important, such as two or more entities that can be used to create a relationship with one another. This aggregation process helps to create more meaningful entities which can derive great results.
- When the ER (Entity - Relationship model) is not able to represent the relationship between any of the present entities in the system then that particular entity can be used to create a new relationship with the other entity. The resultant entity can be used to create a relationship in the Entity-Relationship model.
- When the DBMS has no complex entities but only trivial entities which are not upgradable in the database management system, then it is not possible for future upgrades. In this situation, two or more trivial entities can be used to create a new relationship between these entities and the resultant can be formed as a new complex entity.
When using data in the form of numerical values, the following operations can be used to perform DBMS aggregation:
- Average (AVG): This function provides the mean or average of the data values.
- Sum: This provides a total value after the data values have been added.
- Count: This provides the number of records.
- Maximum (Max): This function provides the maximum value of a given set of data.
- Minimum (Min): This provides the minimum value of a given set of data.
- Standard deviation (std dev): This provides the dispersion or variation of the sets of data. Let’s take a simple example of a database of student marks. If the standard deviation is high, it means the average is obtained by lower number of students than usual, and the lowest and highest marks are higher.
- How to show relationships among relationships? - Aggregation is the technique.
- Abstraction is applied to treat relationships as higher-level entities. We can call it Abstract entity.
- Avoid redundancy by aggregating relationship as an entity set itself.
⭐ Quick MCQs
- What is the difference between specialization and generalization in database design?
Answer
Answer: B. Specialization refers to the process of defining a superclass from a subclass, while generalization refers to the process of defining a subclass from a superclass. Explanation: Specialization involves creating subclasses with more specific characteristics from a superclass with more general characteristics. On the other hand, generalization involves creating a superclass with more general characteristics from subclasses with more specific characteristics.
- What is attribute inheritance in database design?
Answer
Answer: C. The process of transferring attributes from a superclass to a subclass. Explanation: Attribute inheritance is a feature in database design where the attributes of a superclass are transferred to a subclass. This allows the subclass to inherit the characteristics of the superclass.
- What is participation inheritance in database design?
Answer
Answer: D. The process of defining the degree to which an entity participates in a relationship. Explanation: Participation inheritance is a feature in database design where the degree of participation of an entity in a relationship can be defined. For example, an entity can participate in a relationship as a mandatory participant or as an optional participant.
- What is aggregation in a DBMS?
Answer
Answer: B. The process of combining multiple entities into a single entity. Explanation: Aggregation is a feature in a DBMS that allows multiple entities to be combined into a single entity. This is useful in modeling real-world relationships where a whole is made up of smaller parts. For example, a car can be modeled as a single entity made up of smaller entities like wheels, engine, and body.
- How does specialization improve the efficiency of a database design?
Answer
Answer: D. By making the database design more specific and easy to understand. Explanation: By creating subclasses with more specific characteristics from a superclass with more general characteristics, the database design becomes more specific and easier to understand. This results in a more organized and efficient database design, as the data is structured in a way that makes it easier to access and manipulate.
- How does generalization improve the efficiency of a database design?
Answer
Answer: C. By making the database design more flexible. Explanation: By creating a superclass with more general characteristics from subclasses with more specific characteristics, the database design becomes more flexible. This allows for changes to be made more easily in the future, as the superclass can be modified to reflect changes in the subclasses. This results in a more adaptable and efficient database design.
- What is the purpose of attribute inheritance in database design?
Answer
Answer: D. To simplify the database design by reducing the need to duplicate data. Explanation: By transferring attributes from a superclass to a subclass, the need to duplicate data is reduced. This results in a simpler and more efficient database design, as the same data is not stored in multiple places.
- What is the purpose of participation inheritance in database design?
Answer
Answer: C. To define the degree of participation of an entity in a relationship. Explanation: By defining the degree of participation of an entity in a relationship, the relationships between entities in the database can be modeled more accurately. This results in a more accurate and efficient database design.
- What are the benefits of aggregation in a DBMS?
Answer
Answer: D. It makes the relationships between entities in the database easier to understand. Explanation: By combining multiple entities into a single entity, the relationships between entities in the database become easier to understand. This results in a more organized and efficient database design.
- How does the use of specialization, generalization, attribute inheritance, participation inheritance, and aggregation in a DBMS improve the overall design of a database?
Answer
Answer: C. It makes the database design more flexible and easier to understand. Explanation: By using these features in a DBMS, the database design becomes more flexible and easier to understand. This results in a more organized and efficient database, as the data is structured in a way that makes it easier to access and manipulate. Additionally, the use of these features can also reduce the amount of data stored in the database and reduce the need to duplicate data.