Variables and Datatypes in JavaScript
Read This on Github
➡️ What is a Variable?
Explain
A variable in JavaScript is a named storage location for a value. You can use variables to store any type of data, such as numbers, strings, arrays, and objects.
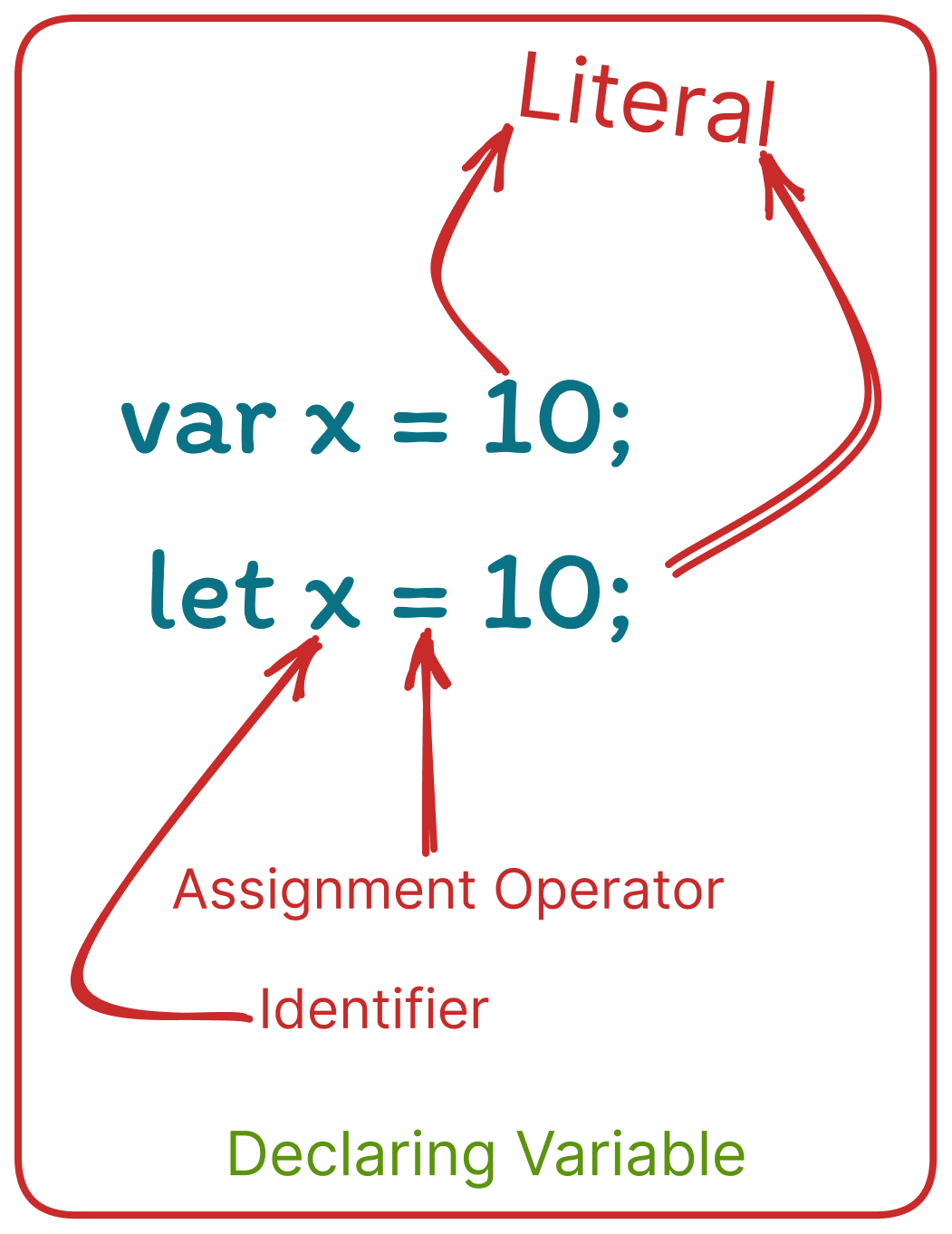
To declare a variable in JavaScript, you use the var keyword, followed by the name of the variable. Here is an example:
var x;This declares a variable named x, but it does not have a value yet. You can assign a value to a variable using the assignment operator =. For example:
var x;
x = 10;This assigns the value 10 to the variable x.
You can also declare and assign a value to a variable in a single line:
var x = 10;In addition to the var keyword, there are two other keywords that can be used to declare variables in JavaScript: let and const. The main difference between var, let, and const is the scope in which they are defined and the ability to reassign their values.
var variables are function-scoped, which means they are only accessible within the function in which they are defined.
let variables are block-scoped, which means they are only accessible within the block of code (delimited by curly braces) in which they are defined.
const variables are also block-scoped, but they cannot be reassigned after they are declared.
Quick Question no 1
How many types of variables are there in JavaScript?
💡Answer
b. Two (2)
Explanation: There are two types of variables in JavaScript: local variable and global variable.
Quick Question no 2
How many declaration keywords of variables are there in JavaScript?
💡Answer
c. Three (3)
JavaScript has three kinds of variable declarations.
var
Declares a variable, optionally initializing it to a value.
let
Declares a block-scoped, local variable, optionally initializing it to a value.
const
Declares a block-scoped, read-only named constant.
➡️ Rules for choosing variable names
Rules for naming variables
1. Use camelCase:
In JavaScript, it is common to use camelCase, where the first word is lowercase and subsequent words are capitalized. For example, a variable representing a user's first name might be calledfirstName.2. Use descriptive names:
It's important to choose names that accurately describe the value that the variable holds. For example, a variable representing a user's age might be calledage, not x or num.3. Avoid using reserved words:
JavaScript has a set of reserved words that cannot be used as variable names. These include words likevar, function, and if.4. Avoid using abbreviations:
While abbreviations can save space, they can also make your code harder to read. Try to use full words rather than abbreviations, unless the abbreviation is well-known and widely understood (such as HTML or CSS). For example,firstName is easier to understand than fn.5. Be consistent:
It's important to be consistent in your naming conventions throughout your code. Pick one style and stick with it to make your code more readable and easier to understand. for example, if you use camelCase for your variable names, you should use camelCase for your function names as well.6. Use lowercase letters:
JavaScript is case-sensitive, sofirstName and firstname are two different variables. It's best to use lowercase letters for your variable names, as this is the convention used by most JavaScript developers.7. Use semicolons:
JavaScript statements are often separated by semicolons. It's best to use semicolons at the end of each statement, even if they are optional.8. Use single quotes:
JavaScript strings are surrounded by single or double quotes. It's best to use single quotes for strings, as this is the convention used by most JavaScript developers.9. Starts with keyword:
JavaScript variables must begin with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign (name, _name, and nameare all valid variable names. However, numbers are not allowed as the first character. For example,1name` is not a valid variable name.By following these rules, you can create clear and easy-to-read variable names that accurately represent the values they hold. This will make your code more maintainable and easier to understand for yourself and others.
Quick Question no 3
Which of the following is a valid variable name?
💡Answer
c. name
JavaScript variables must begin with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign (name, _name, and nameare all valid variable names. However, numbers are not allowed as the first character. For example,1name` is not a valid variable name.
➡️ let vs const vs var
let vs const vs var explain
var, let, and const are three different ways to declare variables in JavaScript. One key difference between these three declarations is the scope of the variables they create.
1. Globally scoped & Block scoped:
varis function-scoped, which means that the variable is only accessible within the function in which it is declared. If avarvariable is not declared within a function, it is accessible globally, which means that it can be accessed from anywhere in the code. Here's an example of declaring a globalvarvariable:
letandconstare block-scoped, which means that they are only accessible within the block in which they are declared. A block is a piece of code surrounded by curly braces, such as anifstatement or aforloop. Here's an example of declaring a block-scopedletvariable:
Block-scoped variables are not accessible outside of the block in which they are declared, unlike var variables which are accessible globally if they are not declared within a function. This can be helpful in preventing unintended behavior and making your code more predictable and maintainable.
2. Var can be re-declared and updated:
- In JavaScript, the
varkeyword is used to declare a variable. Variables declared withvarhave function scope, meaning they are only accessible within the function in which they are declared or within any functions that are nested within that function.
Here is an example of declaring and updating a variable with var:
In this example, the doSomething function declares a variable x and assigns it the value 10. The value of x is then logged to the console. The value of x is then updated to 20 and logged to the console again.
-
It's also possible to re-declare a variable with var within the same scope. For example:
In this case, the variable x is re-declared with the value 20. The value of x that was originally assigned to 10 is replaced by the new value.
- It's important to note that re-declaring a variable with var does not result in an error, but it can lead to confusing or unexpected behavior in your code. It's generally a good practice to avoid re-declaring variables within the same scope.
3. Let can be updated but not re-declared:
In JavaScript, variables declared with the let keyword can be updated or reassigned, but they cannot be redeclared in the same block of code.
-
Here is an example of updating a variable declared with let:
-
Here is an example of attempting to redeclare a variable declared with let:
-
On the other hand, variables declared with the var keyword can be updated or reassigned, and they can also be redeclared within the same block of code.
It's generally recommended to use let instead of var when declaring variables in modern JavaScript, as let provides more precise control over variable declarations and can help prevent unintended behavior in your code.
4. const can neither be updated nor re-declared:
In JavaScript, the const keyword is used to declare a constant variable. Constant variables are variables that cannot be reassigned or redeclared.
Here is an example of declaring a constant variable:
const PI = 3.14;In this example, PI is a constant variable that has a value of 3.14.
- If you try to reassign a value to a constant variable, you will get an error:
PI = 3.14159; // This will throw an error- Similarly, if you try to redeclare a constant variable, you will also get an error:
const PI = 3.14;
const PI = 3.14159; // This will throw an error- Even if you declare with let or var, you will still get an error:
const PI = 3.14;
let PI = 3.14159; // This will throw an error
var PI = 3.14159; // This will throw an errorIt's important to note that the value of a constant variable is still mutable. For example, you can still modify the properties of an object that is assigned to a constant variable:
const obj = {};
obj.name = "John"; // This is allowedHowever, you cannot reassign the object itself to the constant variable:
obj = {}; // This will throw an errorIn summary, const variables cannot be reassigned or redeclared, but the values they hold may still be mutable.
5. Var variables are initialized with undefined let and const are not initialized with undefined in javascript explain with simple example
In JavaScript, variables declared with the var keyword are initialized with the value undefined when they are created. This means that if you declare a variable with var and don't assign it a value, it will have a value of undefined. For example:
On the other hand, variables declared with the let and const keywords are not automatically initialized with a value. If you try to access the value of a let or const variable that has not been assigned a value, you will get a ReferenceError because the variable has not been defined. For example:
- It's important to note that the let and const keywords were introduced in ECMAScript 2015 (ES6) and are generally considered to be better alternatives to var for declaring variables. This is because let and const have more strict rules for variable declarations and can help prevent common coding mistakes.
6. Const must be initialized during declaration unlike let and var
In JavaScript, the const keyword is used to declare a constant variable, which means that the value of the variable cannot be reassigned. The value of a constant variable can be changed if it is an object, but the variable identifier cannot be reassigned.
For example:
const PI = 3.14;
PI = 3.14159; // This will throw an error
const obj = {};
obj.name = "John"; // This is allowed
obj = {}; // This will throw an errorIt is important to note that const variables must be initialized during declaration. This means that you must specify a value for the constant when you declare it.
For example:
const PI; // This will throw an error because PI is not initialized
const PI = 3.14; // This is allowedOn the other hand, the let and var keywords are used to declare variables in JavaScript. These variables can be reassigned and do not have to be initialized during declaration.
For example:
let x;
x = 10;
x = "hello";
var y;
y = 20;
y = false;In general, it is considered best practice to use const whenever possible and only use let or var when reassignment is necessary. This helps to prevent accidental reassignment and makes the code easier to understand.
Quick Question no 4
What is the difference between using the let and var keywords to declare a variable in JavaScript?
💡Answer
Answer: A) let is used to declare variables with block scope, while var is used to declare variables with function scope.
Explanation: In JavaScript, let is used to declare variables that are limited in scope to the block, statement, or expression in which they are used. This is in contrast to the var keyword, which declares variables with function scope, meaning they are accessible throughout the entire function in which they are declared.
Quick Question no 5
What is the difference between using const and let to declare a variable in JavaScript?
💡Answer
Answer: B) const variables cannot be reassigned, while let variables can.
Explanation: In JavaScript, const is used to declare variables that are read-only, meaning they cannot be reassigned. This is in contrast to the let keyword, which declares variables that can be reassigned. It's important to note that the value of a const variable can still be mutable (able to be modified), but the variable itself cannot be reassigned.
Quick Question no 6
Can the value of a const variable be changed in JavaScript?
💡Answer
Answer: C) It depends on how the const variable was declared.
Explanation: In JavaScript, the value of a const variable can be changed if the value is mutable (able to be modified). For example, if a const variable is declared as an array or object, the elements or properties of that array or object can be modified. However, the variable itself cannot be reassigned. If the const variable is a primitive data type (such as a number or string), it cannot be modified or reassigned.